Table of Contents
ToggleIn the current landscape of the digital age, where all information flows through virtual channels and algorithms- and this process shapes our whole online experiences.
Amidst this process, a very new concept of concern arises, and that is data privacy.
We are willingly, mostly, and unwillingly sometimes, leaving all our whereabouts in the form of almost footprints with every click and tap.
If we think in-depth, a very scary question arises, and that is- who has control of our complete online personalities?
Who has taken charge of protecting the extensive repositories of our inclinations, routines, and confidentialities?
A very thin line lies between the delicate balance of our interconnected online lives and protecting our personal information.
Online interactions have become a necessity. It is important to understand data privacy in the case of both individuals and organizations at this point.
Every online transaction, be it a social media post, an e-commerce purchase, or a simple search query, contributes to the collage of our digital identity.
Understanding About GDPR-
Addressing all the above worries about privacy, the European Union (E.U.)- created a big set of rules related to data protection and privacy.
It shows how much the E.U. cares about keeping people’s personal information safe. The main idea behind the GDPR is to give individuals more power over their own data.
So, what does it mean for you and me? Well, the GDPR gives us rights. We can ask companies to show us what personal information they have about us, correct any mistakes, and even ask them to delete it. On the other side, companies have to make sure they’re doing everything they can to keep our information safe. If they don’t follow the rules, they can get fined.
The impact of the GDPR goes beyond just making sure data is stored securely. It makes companies more careful about how they handle our information. They need to encrypt it, tell us if there’s been a data breach, and only collect the data they really need. This means companies all around the world, not just in Europe, have to step up their game when it comes to protecting our information.
But it’s not just about the technical stuff. The GDPR encourages a culture where companies have to be open and honest about how they use our data. They can’t just collect it without asking and must explain why they need it. This openness helps build trust so we can feel more in control of our information when we’re online. It’s like having a set of rules that everyone has to follow to make sure our digital lives are safer and more respectful of our privacy.
Protected Data under GDPR:
These are just examples, and the GDPR covers any information that can directly or indirectly identify a person. It’s a comprehensive approach to protecting a wide range of personal data.
What is UK GDPR?
Before Brexit, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) applied in the UK. This was a set of rules from the European Union (EU) to protect people’s personal information.
Now, after Brexit, the UK has its own version called the UK GDPR. Think of it like the same rulebook but with a few tweaks because the UK isn’t in the EU anymore.
The goal is still to keep your personal data safe, like your name, address, or anything that can identify you. The UK GDPR makes sure that companies in the UK follow these rules. So, even though the UK is doing its own thing now, it’s still serious about protecting your privacy online.
About Compliance and Security-
Data security and compliance are crucial for organizations to protect sensitive information and meet regulatory requirements. Here are practical tips and best practices to ensure compliance-
- Understand Regulations: Stay informed about relevant data protection laws in your industry and region. Whether it’s GDPR, HIPAA, or others, knowing the rules is the first step.
- Data Mapping: Identify where sensitive data is stored, processed, and transmitted within your organization. This includes databases, cloud services, and even employee devices.
- Access Controls: Implement strict access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information. Regularly review and update access permissions based on job roles.
- Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data, both in transit and at rest. This adds an extra layer of protection, making it harder for unauthorized individuals to make sense of the information even if they manage to access it.
- Employee Training: Conduct regular training sessions to educate employees about data security practices and compliance regulations. Human error is a common cause of data breaches, so keeping staff informed is vital.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop a clear and actionable incident response plan. In the event of a data breach, knowing what steps to take promptly can minimize damage and demonstrate compliance efforts.
- Regular Audits: Conduct internal audits to assess data security measures. Regular reviews help identify vulnerabilities and ensure that your organization is continuously improving its data protection practices.
- Data Minimization: Only collect and retain data that is necessary for your business operations. Avoid unnecessary accumulation of sensitive information to minimize risks.
- Vendor Management: If you work with third-party vendors, ensure they also adhere to data protection standards. Include data security clauses in contracts and regularly assess their compliance.
- Privacy by Design: Integrate data protection measures into the design of your systems and processes from the beginning. This ensures that privacy is a fundamental consideration rather than an add-on.
- Document Policies: Clearly document your data security and compliance policies. This helps in internal communication and serves as a reference point for employees.
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of changes in data protection laws and update your strategies accordingly. Compliance is an ongoing process, and staying current is key to avoiding penalties.
Data Breach Consequences under GDPR-
Understanding the consequences is essential for organizations to prioritize data security measures and ensure compliance with GDPR.
The financial and legal fallout from a data breach can be severe, emphasizing the importance of cybersecurity practices and adherence to privacy regulations.
Data subjects (individuals whose data is breached) can take legal action against the organization for damages resulting from the breach.
Remediation Costs
Organizations must invest in rectifying the breach, which includes identifying the cause, notifying affected parties, and implementing security improvements.
Loss of Business
The fallout from a data breach can result in customers losing trust, leading to reduced business and potential revenue loss.
Increased Insurance Costs
Following a breach, organizations may face higher premiums when renewing cybersecurity insurance policies.
Regulatory Compliance Costs
Besides fines, organizations may need to invest in measures to bring their data processing practices in line with GDPR requirements.
What is the Importance of Data Protection Laws?
- Privacy protection: Data protection laws ensure individuals have control over their personal information, preventing unauthorized access or usage.
- Ethical Handling: Upholding these laws promotes ethical data handling practices, fostering trust between individuals and organizations.
- Preventing Exploitation: Regulations prevent the misuse of personal data, curbing the potential for discrimination, exploitation, or manipulation.
- Trust Building: Adherence to data protection laws builds trust in the digital ecosystem, encouraging people to engage online without fear of privacy breaches.
- Individual Empowerment: Such laws empower individuals, granting them the right to know, control, and erase their data, reinforcing a sense of control over their digital identity.
- Global Standards: Establishing ethical data practices sets global standards, promoting responsible behaviour among businesses and governments in handling personal information.
GDPR Requirements and Compliance Checklist-
Compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) involves several key steps.
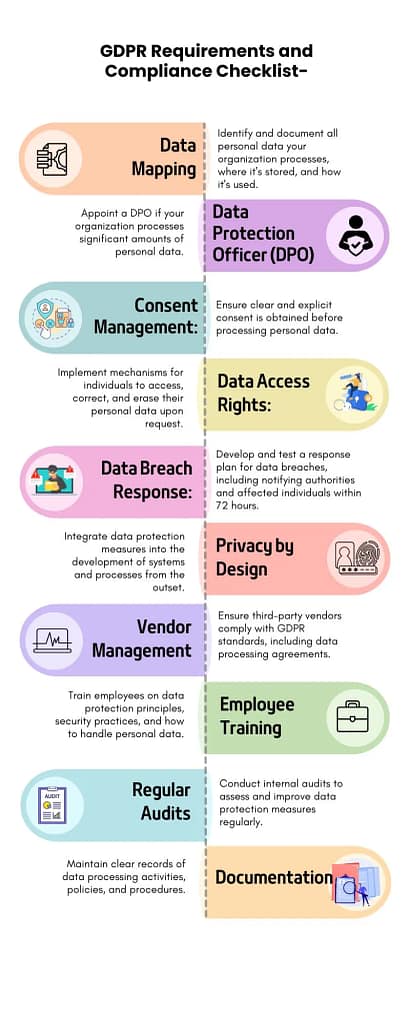
GDPR Data Protection Principles-
The GDPR is anchored in seven core principles, each playing a crucial role in data protection-
Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency:
- Significance: Processing personal data must be lawful, fair, and transparent. Individuals should know how their data is used.
- Purpose Limitation:
- Significance: Data should be collected for a specific, explicit purpose and not used for anything incompatible with that purpose.
- Data Minimization:
- Significance: Collect only the data necessary for the intended purpose. Avoid excessive or irrelevant information.
- Accuracy:
- Significance: Ensure data is accurate and up-to-date. Take steps to rectify inaccuracies promptly.
- Storage Limitation:
- Significance: Keep personal data for the minimum necessary time. Regularly review and delete unnecessary information.
- Integrity and Confidentiality (Security):
- Significance: Implement security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, alteration, or disclosure.
- Accountability:
- Significance: Demonstrate compliance by maintaining documentation, conducting impact assessments, and assigning responsibility for data protection.
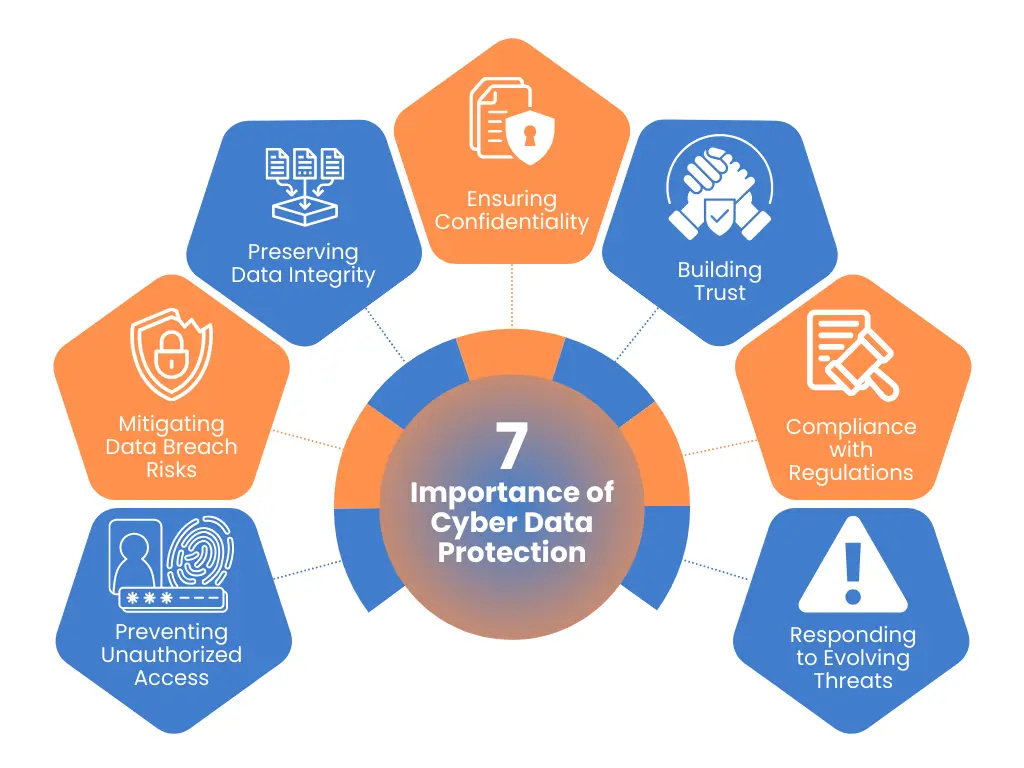
Why is it so important to be prepared for GDPR compliance?
Ensuring GDPR compliance is very important for organizations due to the significant consequences of non-compliance.
Early preparation is crucial as it allows organizations to effectively understand and implement the necessary measures to protect individuals’ personal data.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) mandates rules regarding processing personal information, and failure to comply can result in hefty fines, legal repercussions, and reputational damage.
By preparing in advance, organizations can establish data protection practices, implement necessary technological protection, and educate their staff on privacy measures, creating a culture of awareness and responsibility.
Early compliance safeguards against financial penalties and builds customer trust, as they are assured that their personal data is handled ethically and securely.
CONCLUSION-
Data privacy is not just a legal obligation; it’s a fundamental human right in the digital age. Our online existence deserves the same protections as our offline lives.
But the fight for data privacy is not one fought alone. We, as individuals, must actively engage in this crucial conversation. Share your experiences with data privacy regulations, raise awareness amongst your circles, and demand accountability from organizations that handle your personal information. Remember, your voice matters and your actions can contribute to a future where data privacy is not merely a privilege but a fundamental right everyone enjoys.
Further Resources-
- The European Commission’s GDPR website: https://gdpr.eu/
- The International Association of Privacy Professionals (IAPP): https://iapp.org/
- The Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF): https://www.eff.org/
- The Future of Privacy Forum (FPF): https://fpf.org/
Frequently Asked Questions (FaQ)
What are the privacy trends for 2024?
Data Privacy Trends 2024:
- Regulation Expansion: More countries are enacting comprehensive data privacy laws, like the EU’s AI Act and GDPR, pushing global coverage.
- Transparency Demands: Users want more precise explanations of how their data is collected, used, and shared. AI applications will face scrutiny.
- Workplace Adoption: Privacy measures are increasingly necessary for employee data handling, monitoring, and AI use.
- Advanced Encryption: Quantum-resistant encryption algorithms will gain prominence for more robust data protection.
- AI for Mitigation: Leveraging AI to identify and address emerging privacy risks in complex systems.
What is the future of data privacy?
Future of Data Privacy:
- Balancing Innovation and Privacy: Finding ways to allow innovation while protecting individual rights will be crucial.
- Empowering Users: Providing users with more control over their data and choices about its use will be critical.
- Technological Solutions: Advances in privacy-enhancing technologies like homomorphic encryption and differential privacy will offer new possibilities.
- International Cooperation: Global collaboration on data privacy standards and enforcement will be crucial.
Which country has the most robust data privacy laws?
Strongest Data Privacy Laws:
- European Union: The GDPR sets a high bar for data privacy rights and protections.
- California: The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) gives individuals broad rights to access, delete, and opt out of data sharing.
- Brazil: The General Data Protection Law (LGPD) grants similar rights as the GDPR and applies to any data of Brazilian citizens processed abroad.
Is data privacy a right in India?
Data Privacy in India:
- Right to Privacy: The Indian Constitution recognizes privacy as a fundamental right.
- Data Protection Bill 2024: Still awaiting passage, this bill aims to regulate data collection, storage, and processing by companies.
- Current Law: Personal data protection is governed by sectoral laws like the IT Act 2000 and Information Technology (Reasonable Security Practices and Procedures for Sensitive Personal Data) Rules 2011.
Is the Data Protection Bill 2024 passed?
Cybersecurity Trends 2024:
- Ransomware Evolution: Attacks will become more targeted and sophisticated, impacting critical infrastructure.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Compromised software vendors or third-party services pose increasing risks.
- Cloud Security Challenges: Securing cloud environments and protecting data in the cloud will be crucial.
- Phishing & Social Engineering: These methods will remain prevalent, requiring user awareness and training.
- AI-powered Threats: Malicious actors will leverage AI for automated attacks and evasion techniques.
What is the data privacy law in India in 2024?
Dangers of AI in 2024:
- Bias and Discrimination: Algorithmic bias can lead to unfair outcomes in hiring, loan approvals, and even criminal justice.
- Privacy Violations: AI systems can inadvertently collect and use sensitive data without proper safeguards.
- Deepfakes and Misinformation: Malicious actors can use AI to create realistic but fake videos and texts, spreading disinformation.
- Autonomous Systems Security: Ensuring the safety and security of self-driving cars and other autonomous systems is crucial.
How can data privacy be compromised in AI systems?
Data Privacy and AI:
- Data Poisoning: Attackers can manipulate training data to introduce bias or errors into AI models.
- Model Explainability: Understanding how AI models make decisions is essential for accountability and trust.
- Differential Privacy: Techniques that add noise to data while preserving statistical insights offer privacy guarantees.
How do you think Equifax has transformed after the data breach?
Equifax and Data Breaches:
- Equifax implemented significant security improvements, including increased employee training, penetration testing, and vulnerability management.
- They invested in data encryption, multi-factor authentication, and improved monitoring systems.
- They established a data security council and appointed a Chief Data Officer to oversee data privacy practices.
What policies can be implemented to prevent data breaches?
Preventing Data Breaches:
- Implement robust security policies and procedures, including regular employee training.
- Use secure systems and software, and patch vulnerabilities promptly.
- Encrypt sensitive data and restrict access to authorized personnel.
- Regularly monitor systems and logs for suspicious activity.
- Have a well-defined incident response plan in place.
How can a data breach be stopped?
Stopping Data Breaches:
- Early detection and response are crucial. Employ advanced security tools and threat intelligence.
- Isolate compromised systems and contain the breach to prevent further damage.
- Notify affected individuals and authorities promptly.
- Conduct a thorough investigation to identify the root cause and prevent future occurrences.
What are the consequences of a data breach under GDPR?
GDPR Consequences of Data Breaches:
- Fines of up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher.
- Reputational damage and loss of customer trust.
- Potential legal action from individuals whose data was compromised.
Why are there still so many data breaches?
Data Breaches Still Happen:
- Human error remains a significant factor, such as phishing attacks or falling for social engineering scams.
Why should I be concerned with data privacy?
You should be concerned with data privacy for several reasons:
- Personal harm: Leaked data can be used for identity theft, financial fraud, blackmail, discrimination, and more. This can lead to significant financial losses, damage to your credit score, and emotional distress.
- Erosion of trust: When your data is breached, it erodes trust in the companies and organizations you interact with. This can make you hesitant to share information online or engage in digital activities.
- Limited control: Companies often collect vast amounts of data about you without explicit consent, leaving you with little control over how it’s used or shared. This can feel like a violation of your privacy and autonomy.
- Unequal benefits: The benefits of data collection often flow to companies and governments, while individuals bear the risks. This creates an imbalance of power and raises concerns about fairness and ethical data practices.
- Future implications: As technology advances and data becomes even more valuable, the potential consequences of data breaches will likely become more significant. By taking steps to protect your privacy now, you’re preparing for the future.
What are the consequences of reporting a security breach?
Reporting a security breach can have both positive and negative consequences:
Positive:
- Protection for others: By reporting a breach, you potentially help prevent others from being harmed.
- Accountability: Reporting can hold companies accountable for data security failures and encourage them to improve their practices.
- Improved security: In the long run, reporting improves overall security standards by raising awareness and prompting action.
Negative:
- Retaliation: In some cases, companies may retaliate against individuals who report breaches, though this is illegal in many regions.
- Stress and hassle: Reporting a breach can be stressful and time-consuming, involving paperwork, investigations, and potential legal proceedings.
- Reputation damage: Your personal information may become public during the breach investigation, potentially impacting your reputation.
Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to report a breach is a personal one. Weighing the potential benefits and risks, along with your circumstances, is essential.
Can you define a security breach and a data breach?
Security breach: A security breach is any unauthorized access to, disclosure, destruction, use, modification, or denial of control over computer systems, networks, or data. This can be caused by intentional attacks, accidents, or system vulnerabilities.
Data breach: A data breach is a type of security breach that involves explicitly the unauthorized access to, disclosure, or acquisition of sensitive personal information. This could include names, addresses, Social Security numbers, financial information, medical records, or other sensitive data.




Your analysis of data privacy trends in 2024 is truly exceptional! Your blog post provides a comprehensive overview of the current landscape, and I’m particularly impressed by several key points:
Firstly, your clear and concise explanation of GDPR is incredibly valuable. Demystifying such a complex regulation makes it accessible to a broader audience, which is essential in today’s digital age.
Secondly, your emphasis on the importance of cybersecurity resonates strongly. In a time when cyber threats are increasingly sophisticated, highlighting the need for robust cybersecurity measures is crucial for safeguarding data integrity.
Lastly, your exploration of emerging trends, from data localization laws to privacy-enhancing technologies, offers valuable insights into the future of data privacy. It’s thought-provoking and provides a solid foundation for understanding where the field is heading.
Overall, your blog post is a must-read for anyone interested in staying informed about data privacy. It’s evident that Networsys Technologies has a deep understanding of this complex field, and I look forward to reading more from you in the future!